Grid-following converter (GFl)
The name Current Controlled Voltage Source Inverter (CCVSI) is introduced in [1] for grid-following converters, a type of DC/AC converters that measure the voltage magnitude and angle at their point of connection using a phase-locked loop (PLL), and supply at that point the active and reactive power required by controlling the injected current.
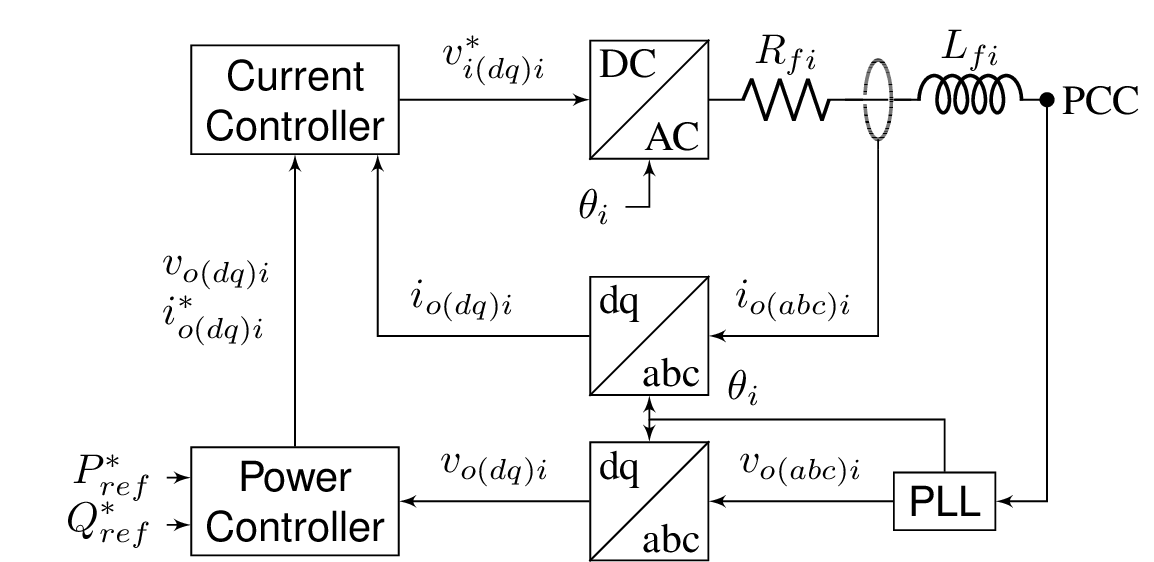
The abc/dq blocks represent the well-known Park's transform, a reference frame change which transfoms the 3 phase voltage signal to a rotating \( dq0\) frame. Considering only balanced voltage, homopolar component can be discarded. This model considers a power invariant Park's transform, in which the power is: $$ P = v_{odi}i_{odi} + v_{oqi}i_{oqi} \hspace{2cm} Q = v_{oqi}i_{odi} - v_{odi}i_{oqi} $$
Level 0 control
In general, the inner current controller of an electronic converter is not considered part of the hierarchical microgrid control, and are included in a control layer level 0 control. This is the fastest control layer. Among other purposes, it is usually in charge of following the inner current reference and limitating the output current of the converter when a fault occurs.Current Controller
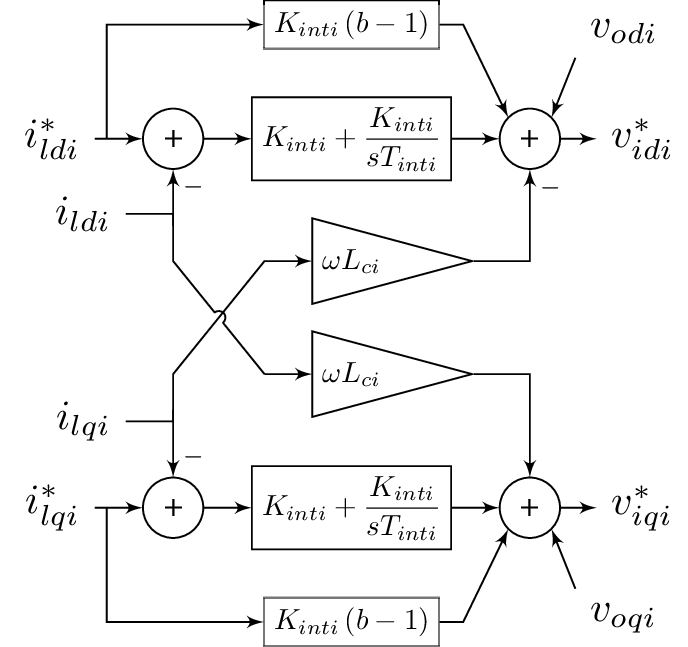
In this model, the user can choose the complexity of the voltage and current controllers between dynamic behavior or static behavior.Dynamic current controller